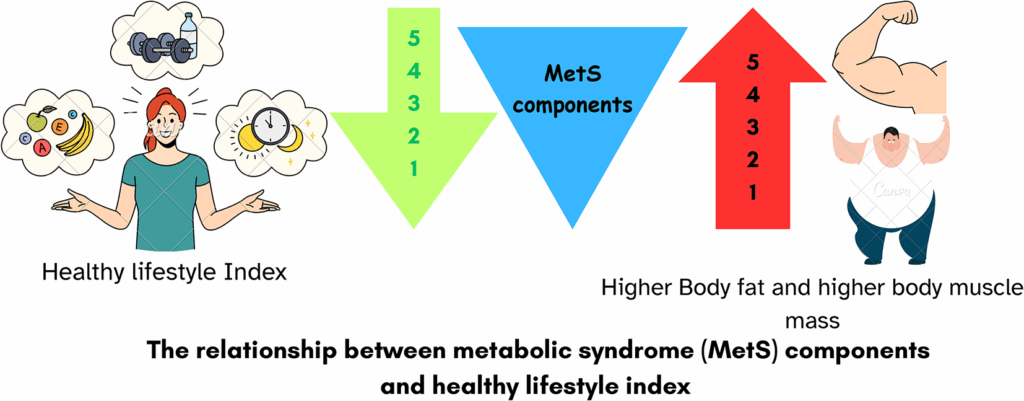
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is highly prevalent, and it is associated with unhealthy lifestyle risk factors that can be easily modified. To evaluate body composition, the adults’ eating behavior score (AEBQ), and the healthy lifestyle index (HLI) with metabolic syndrome (MetS) in female Jordanian adults. A cross-sectional study was conducted among 656 females in Jordan. Sociodemographic, anthropometric, blood pressure, and biochemical data were collected. The HLI and AEB questionnaire (AEBQ) was completed, and the waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) and body mass index (BMI) were calculated. MetS was determined based on NCEP-ATPII criteria. Participants with MetS had significantly higher percentages of body fat (44.15 ± 6.37%) and body muscle mass (25.7 ± 4.56%). The mean HLIBMI or HLIWHR for participants with MetS (10.7 ± 1.51 and 11.6 ± 2.03, respectively) was significantly lower than for participants without MetS (11.5 ± 2.37, p = 0.003, and 12.4 ± 2.37, p = 0.004, respectively). Participants with five MetS components had significantly the highest % of body fat (46.07 ± 4.80, pRead More
Evaluating body composition, the eating behavior scale, and the healthy lifestyle index in female Jordanian adults with metabolic syndrome: a cross-sectional study – Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome
Related Posts
Add A Comment